Introduction to the Wave Principle
Ralph Nelson Elliott was one of very first person who believed that he could predict the stock market by studying the repeating price patterns in the price series. The Wave Principle from Elliott states that the wave patterns in different scales are repeating and superimposing on each other forming complex wave patterns. If harmonic pattern directly focuses on the short patterns made up from five points, the Wave Principle, developed by Ralph Nelson Elliott, describe how the financial market evolve to meet the equilibrium with the repeating wave patterns, equilibrium fractal waves. The advantage of Elliott Wave theory is that it is comprehensive as the theory provides multiple trading entries on different market conditions. With Elliott Wave theory, traders can perform both momentum trading and mean reversion trading. The disadvantage of Elliott Wave theory is that it is more complex comparing to other trading techniques. In addition, there are still some loose ends in detecting Elliott wave patterns. For this reason, many traders heavily criticize the lack of scientific methods of counting Elliott Waves.
Elliott Wave theory received good attention from many traders and investors for several decades. Elliott Wave theory is a useful technique to deal with the financial market with the dominating Equilibrium Fractal-Wave process. For the financial market with strong Equilibrium Wave process (2nd, 3rd and 4th columns in the Price Pattern Table), traders must use alternative methodology over Elliott Wave techniques because Elliott Wave Theory is not meant to deal with Wave process. Seasonality or other cyclic fluctuations can be dealt better with other techniques. For example, Seasonal Exponential Smoothing, Fourier Transform, Principal Component Analysis or Wavelet Transformation might do better job for such a case. Some literature review and empirical research can yield helpful insight on which market trader can trade better with Elliott Wave Theory. In our Book, we will introduce the fundamentals of the Wave Principle. At the same time, we will introduce the template and pattern approach towards more scientific wave counting for traders.
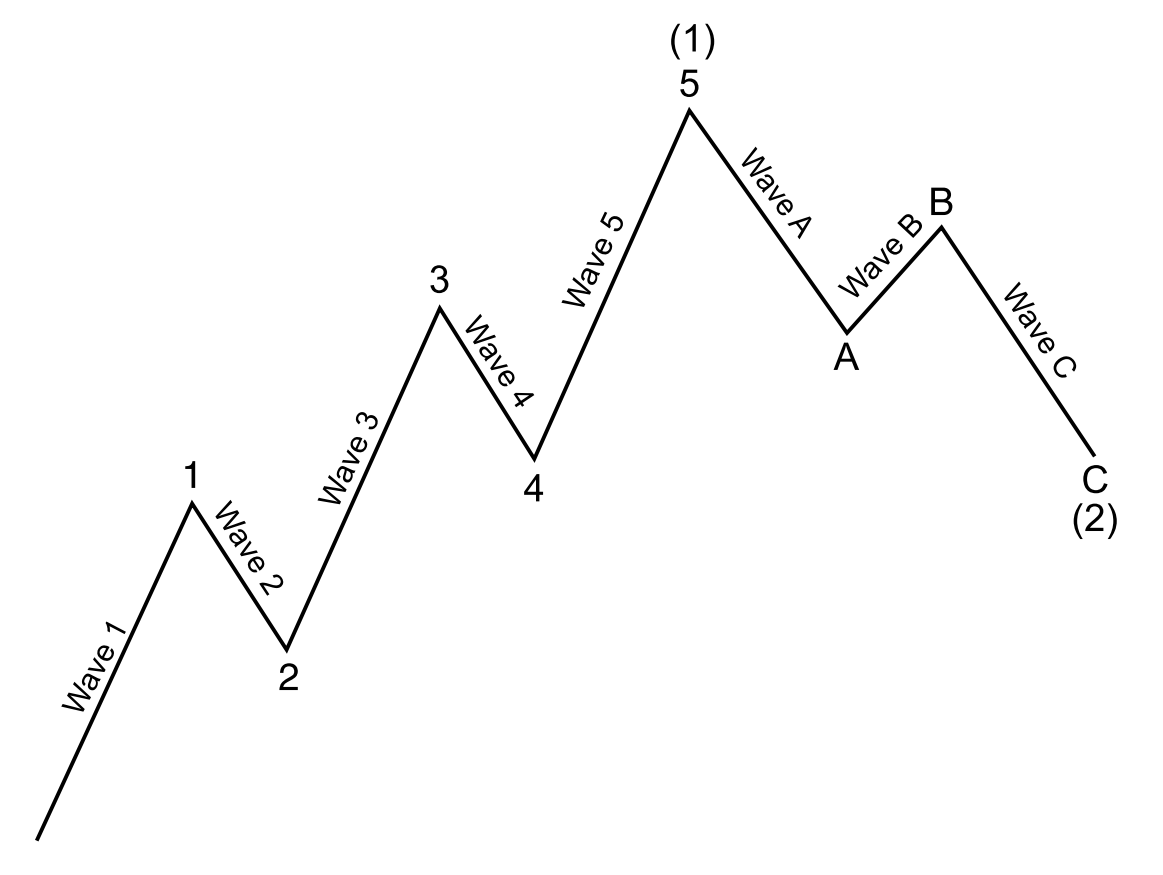
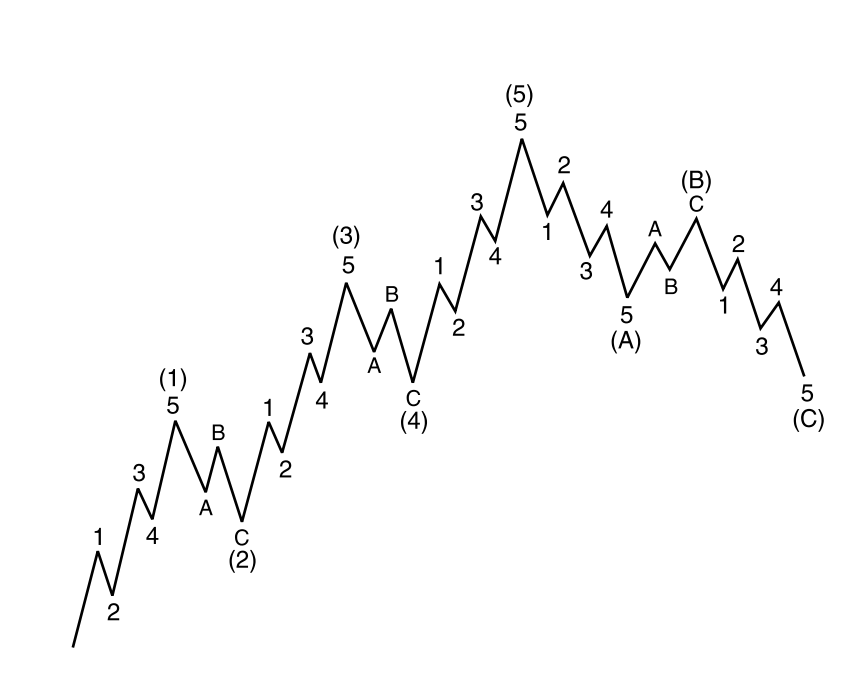
The Wave Principle states that the crowd or social behaviour follows a certain wave patterns repeating themselves. The Wave Principle identifies two wave patterns. They are impulse and corrective wave. Often, the term impulse wave is interchangeably used with the motive wave. Two terms are identical. Both motive and impulse wave progress during the main trend phase whereas the corrective wave progress during the corrective phase against the main trend. In general, the Impulse Wave has a five-wave structure, while the Corrective Wave have a three-wave structure (Figure 5-1). It is important to understand that these wave structures can override on smaller wave structure to form greater wave cycle (Figure 5-2). Elliott Wave theory is useful in identifying both trend market and correction market. As the Elliott Wave Theory already assumes that price progresses in the Fractal-Wave form, they do not suffer from lagging of price like the smoothing algorithm based technical indicators do.
Figure 5-1: Illustrative example of five impulse wave and three corrective wave structure.
Figure 5-2: Lesser Impulse and corrective wave forming more complex wave patterns.
About this Article
This article is the part taken from the draft version of the Book: Scientific Guide to Price Action and Pattern Trading (Wisdom of Trend, Cycle, and Fractal Wave). Full version of the book can be found from the link below:
Elliott Wave Trend is the most advanced Elliott Wave Trading software, which helps you to trade with various Elliott Wave patterns like Wave .12345 pattern and Wave .ABC and Wave .ABCDE, and so on. Elliott Wave Trend was built on the concept of Precision Trading with Elliott Wave Structure Score. Our Elliott Wave Trend is professional tool for professional trader. Elliott Wave Trend is available in both MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 platform.
YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/Oftml-JKyKM
Our Elliott Wave Trend is available in both MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 version. Here are the links to Elliott Wave Trend.
https://algotrading-investment.com/portfolio-item/elliott-wave-trend/
https://www.mql5.com/en/market/product/16472
https://www.mql5.com/en/market/product/16479
EFW Analytics provide the graphic rich and fully visual trading styles. In default trading strategy, you will be looking at the combined signal from Superimposed pattern + EFW Channel or Superimposed pattern + Superimposed Channel. In addition, you can perform many more trading strategies in a reversal and breakout mode. You can also run two different timeframes in one chart to enforce your trading decision. Sound alert, email and push notification are built inside the indicator.
Below is the link to the EFW Analytics:
https://algotrading-investment.com/portfolio-item/equilibrium-fractal-wave-analytics/
https://www.mql5.com/en/market/product/27703
https://www.mql5.com/en/market/product/27702
Related Products